How Long Does a Felony Stay on Your Record? Confusing Law Explained
Asking how long a felony stay on your record is common when considering nearly 24 million Americans had a felony conviction in 2019 alone per the United States Senate Joint Economic Committee.1
Despite how often felony charges arise, the laws surrounding felonies and background checks can be confusing because each state has its own laws and policies regarding how long felony convictions can affect obtaining employment, career certifications, licensure, or finding sustainable housing.
However, you can check to see if a felony is on anyone’s record by simply filling out the form or reading about applicable state laws below. No matter the case, the confusing laws are explained followed by an in depth guide to what individuals can do to lessen the effects of a felony record.
How the Duration of Felonies Staying on Your Record Affect Background Checks & Future Opportunities
There are a number of negative impacts a felony record can have on a person’s future and the duration felonies stay on your record can affect employment opportunities as well as housing opportunities and other aspects of daily life.
Felony convictions can also impact a person’s Constitutional Rights. For example, United States Code 922(g) and 922(n) prohibit anyone who has been convicted of a felony from possessing or purchasing a firearm or ammunition.

Until the records of felony are sealed or expunged, they are public records and will have an impact.
Although each state has its own regulations regarding felonies as public records, as well as the amount of time that must pass before a person is eligible to have the record sealed or erased.
Federal laws also play a role in how long certain information can be used in background checks or viewed such as the Fair Credit Reporting Act regarding arrest records and guidance by the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission.2, 3
No matter the case, as long as the felony record is open to the public, it can negatively affect a person’s daily life and can have an impact for years or a lifetime.
How Many Years Does a Felony Stay on Your Record in Each State?
For the most part, a criminal record (from infractions to felonies) is a permanent record unless laws specifically require they be removed or sealed after a certain period of time, or unless they are expunged (meaning, a judge has ordered the record to be sealed or destroyed).
Each state has its own laws guiding how long felonies stay on a person’s criminal record. The table below provides information on how long felonies stay on a person’s record before they are eligible to be removed via expungement or by sealing the record.
Each state can have various wait times for each classification of a felony. Some felonies are automatically ineligible for expungement due to the nature of the offense.
Classes of Felonies & Their Waiting Periods by State
Felony charges or convictions are for crimes of a particularly serious nature. The greater the harm caused to an individual or society, the higher the classification for a felony. For example, murder is the highest classification for felonies and is usually called Class 1 or Class A felonies.
Lesser felonies could be the possession of controlled substances (drugs) in larger amounts than that for personal use. These can be classified as Class D or Class 4 or 5 felonies. Even lesser felonies are considered much more serious than misdemeanor charges.
The greater the felony classification the greater the punishment for convictions. The classification also determines if a felony charge is eligible for expungement or sealing in states that allow felony convictions to be expunged.
Some states only use misdemeanor or felony to designate the seriousness of the charge and dictate the level of punishment based on the degree or amount of harm caused. For example, Minnesota simply designates felonies as violent or non-violent by statute.4
When considering how long a felony remains on your record, refer to the tables below to find the waiting period to seal or expunge a felony record in each state based on felony class for adult convictions. However, a juvenile record generally cannot be used against you because they are not considered public records, though exceptions may apply.
Alabama
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class A-B |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Class C-D |
5 years |
Alaska
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Felony convictions in Alaska are ineligible for expungement |
Arizona
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class 1 |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Class 2-3 |
10 years |
| Class 4-6 |
5 years |
Arkansas
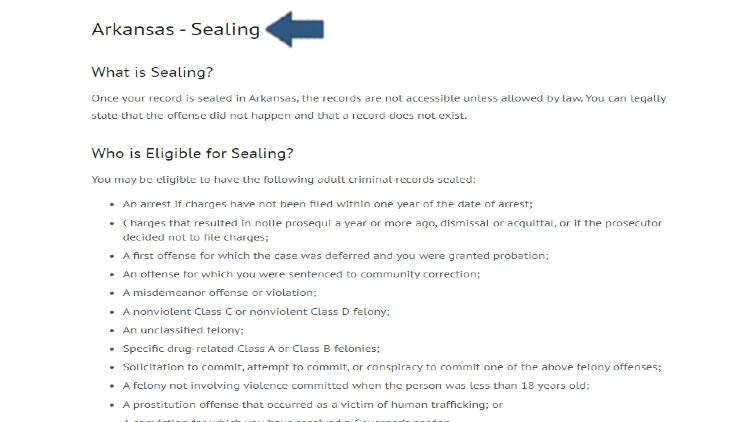
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class A-B |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Class C, D, and Unclassified (non-violent felonies) |
5 years |
California
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Felony convictions in California are ineligible for expungement or sealing; however, they can be reopened and reduced to misdemeanor charges by the court. Once reduced to a misdemeanor they may be eligible for expungement. |
Colorado
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class 1-2 |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Class 3-6 |
3 years |
Delaware
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class A-C |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Class D-F and Unclassified |
10 years |
Florida
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Felony convictions in Florida are ineligible for expungement. |
Georgia
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Georgia does not separate crimes by felony classification like other states. Each felony crime carries its own minimum and maximum sentence as designated by the statute. Only pardoned felony convictions can be expunged. |
Hawaii
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Felony convictions in Hawaii are ineligible for expungement |
Idaho
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Felony convictions in Idaho are ineligible for expungement |
Illinois
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class 1-4 |
Ineligible for sealing or expungement |
| Felony convictions in Illinois are ineligible for expungement unless the convictions have been vacated or pardoned and a three-year waiting period has passed. |
Indiana
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Murder |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Level 1-5 |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Level 6 |
8 years |
Iowa
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Felony convictions in Iowa are ineligible for expungement, only misdemeanors may be expunged. |
Kansas
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class A*-C and Unclassified |
5 years |
| Class D-E |
3 years |
| Unclassified |
5 years |
*Specific homicide, sexual assault, or crimes against children are automatically ineligible for expungement regardless of felony classification.
Louisiana
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| 1st and 2nd Class |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| 3rd Class |
15 years |
Maine
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Felony convictions in Maine are ineligible for expungement |
Maryland
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Maryland does not break felonies up into classifications like other states. Each felony charge has a degree assigned based on the circumstances. The following felonies may be eligible for expungement after 15 years waiting period from the date sentence completed: theft, certain drug possession charges, and burglary. |
Massachusetts
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Massachusetts does not break felonies up into classifications like other states. Each felony charge has a degree assigned based on the circumstances. Most felonies can be expunged after a 7-years waiting period with exceptions for violent felonies or felonies of moral turpitude. |
Michigan
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class A-C |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Class E-H |
10 years |
Minnesota
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Violent Felonies |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Low-Level (Non-Violent Felonies) |
5 years |
| Minnesota designates felonies as either violent or non-violent and does not have a degree or class system to separate felony crimes. |
Mississippi
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
Mississippi only allows expungement for the following specific felony convictions:
- Passing a bad check
- Controlled substance or paraphernalia possession
- Obtaining property under false pretense
- Certain larceny charges
- Malicious mischief charges
- Felony level shoplifting
The wait time to request expungement is 5 years. |
Missouri
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class A-C |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Class D-E |
7 years |
Montana
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Felony convictions in Montana are ineligible for expungement |
Nebraska
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Felony convictions in Nebraska are ineligible for expungement |
Nevada
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class A |
10 years |
| Class B-C |
5 years |
| Class D-E |
2 years |
New Jersey
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| 1st and 2nd Degree |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| 3rd and 4th Degree |
10 years |
New Mexico
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| First Degree |
10 years |
| Second Degree |
8 years |
| Third Degree |
6 years |
New York
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class A-E Violent Felonies |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Class B-E Non-Violent Felonies |
10 years |
North Carolina
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class A-G |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Class H-I |
10 years |
North Dakota
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class AA-C |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Generally, felonies in North Dakota are ineligible for expungement or sealing unless the following criteria exist: victims of human trafficking, conviction is vacated due to DNA evidence, and arrest was unconstitutional. |

Ohio
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| 1st and 2nd Degree |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| 3rd-5th Degree |
5 years |
Oklahoma
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Violent Felonies |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Non-Violent Felonies |
5 years |
| Oklahoma designates felonies as either violent or non-violent and does not have a degree or class system to separate felony crimes. |
Oregon
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class A |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Class B (non-person offenses) |
7 years |
| Class C |
5 years |
Pennsylvania
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| 1st-3rd Degree |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Pennsylvania only expunges or seals felony records when the person convicted reaches the age of 70 or 3 years after the death of the person convicted. |
Rhode Island
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Violent Felonies |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Non-Violent Felonies |
10 years |
| Rhode Island designates felonies as either violent or non-violent for each criminal offense and does not have a degree or class system to separate felony crimes. |
South Carolina
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Felony convictions in South Carolina are ineligible for expungement or sealing. |
South Dakota
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class A-C and Class 1 |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Class 2-6 |
5 years |
Tennessee
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class A-B |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Class C-E |
10 years |
Texas
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Capital, 1st-3rd Degree and State Jail Felonies |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Texas only allows felony expungement for non-convictions (dismissals, not guilty, or overturned in appeal or pardoned). |
Utah
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Capital Felony and 1st Degree |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| 2nd-3rd Degree (Non-violent felonies) |
7 years |
Vermont
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
Vermont does not break felonies up into classifications like other states. Each felony charge has a degree assigned based on the circumstances. Only the felonies below can be expunged:
- Burglary of an unoccupied dwelling
- Passing a forged instrument
- Grand larceny charge
- Felony criminal mischief
- Fraud or deceit-related charge
- Growing or possessing marijuana
- Having possession of cocaine, LSD, heroin, depressants, stimulants, narcotics, methamphetamine, ephedrine/pseudoephedrine, hallucinogenic drugs, ecstasy
- Any felony is pardoned unconditionally by the governor.
The wait time to file for expungement is 5 years. |

Virginia
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class 1-2 |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Class 3-4 |
20 years |
| Class 5-6 |
10 years |
Washington
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Class A-B |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Class C (Non-violent felonies) |
5 years |
West Virginia
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record* |
| Class 1 |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Class 2-6 (Non-violent felonies) |
3-5 years |
*Certain drug convictions can be expunged in 3 years, other felonies in the same classification have a 5-years waiting period.
Wisconsin
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record* |
| Class A |
Ineligible for expungement or sealing |
| Class B-I (Non-violent felonies) |
5 years |
*Expunging records are only available for a first-time offender of a non-violent felony committed while the person was under the age of 25.
Wyoming
| Felony Classification |
Waiting Period to Seal or Expunge Record |
| Wyoming only designates felonies as violent or non-violent felonies. Most non-violent felonies can be expunged after a 10-year waiting period. |
Even in states that allow expunging or sealing records, it’s important to note which felonies may not be eligible as well.
What Type of Felonies Can Never Be Expunged in Any State?
While some states have very relaxed expungement laws, there are certain felonies that are never eligible for sealing or erasing. These offenses include the following:
- Murder
- Rape
- Certain assault charges involving deadly weapons and serious bodily injury
- Sexual offenses against children
- Most capital offenses
- Most arson charges
- Crimes related to terrorism
- Federal felonies
Felony charges and convictions can follow a person for a lifetime and may show up each time the person undergoes a background check.
How Long Does a Felony Stay on a Background Check?
The number of years a felony will stay on a person’s record for a background check varies from state to state.
Generally, it’s 7 to ten years depending on the state; however, some states set no limits on how far back felony convictions may be considered when making employment or housing decisions.
This is often confusing because the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) sets a 7-year limit on the use of adverse action on a background check, but this primarily concerns information related to credit history and arrests, not criminal convictions.5
Each state has its own “lookback” period outlining how far criminal history can be considered when doing a background check. How long a felony stay on a background check varies from state to state.
States Where Felonies Stay On Background Check Reports for a Minimum of 10 Years
States that have not strictly adopted the seven-year lookback period or search limits allow a deeper dive into a person’s criminal history. Several of these states follow a 10-year period; however, this represents the minimum duration a felony conviction might appear on both a free criminal background check and paid versions as well.
Some states do not put any limits on how far back an employer can go for felony records. The states that have a minimum 10-year lookback period include the following:
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arkansas
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Florida
- Georgia
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Nebraska
- New Jersey
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
States Where Felonies Show Up on Background Checks for 7 Years
Some states follow the FCRA guidance for credit checks and have a seven-year lookback period for criminal history. This allows those with older felony convictions and no other criminal history to have a better chance at employment opportunities.
The lookback period is for most employment; however, certain positions can require a long criminal history search. The states that have a seven-year lookback provision include:
- Arizona
- California
- Colorado
- Hawaii
- Kansas
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Montana
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Mexico
- New York
- Texas
- Washington
Even with limited lookback periods, having a felony on a person’s record can cause issues with housing, employment, and licensure.
How to Expunge Your Felony & Get it Off of Your Record
A felony can severely limit a person’s ability to apply for professional licensure, obtain gainful employment or get housing. In some instances, it can even impact a person’s right to vote or exercise other rights.
Expunging or sealing a felony conviction can help give the applicant a better chance to get a job or lease a home or apartment, but the process can be daunting. The length of stay of a felony on your record depends on how quickly one can get it expunged or sealed, the laws in each state, and the type of felony charge.
The following states have automatic expungement laws for felony non-convictions (charges that were never tried, were dismissed or dropped, or were vacated). However, whether dropped charges show up on a background check is a separate matter, and surprisingly enough, most of the time they do appear.
Despite them showing up on background checks in some cases, Clean Slate Laws allow for the automatic clearing of records. Seven states have passed legislation to date.
Other states that are not Clean Slate states require a person to request sealing or expunging the record before it can be removed. The process varies from state to state but in general, individuals should seek out legal aid to ensure the process goes smoothly.

For example, New Jersey allows individuals to request expunging a felony from their record online using a portal specifically for this purpose.6
In Oklahoma, however, the person must file a petition with the court and pay a fee to request the expungement of the record. Additionally, they cannot have been charged or convicted of another offense within 7 years prior to the request, and at least 5 years have passed since the completion of sentencing and the petition to expunge.7
Other states do not allow the expungement of felony convictions at all. These states are Alaska, California (felonies that have been reduced to misdemeanors may be eligible for expungement), Hawaii, Idaho, Iowa, Maine, Montana, Nebraska, South Carolina, and Texas.8
While a felony can be a huge roadblock to someone seeking employment or looking for housing, there are some things a person can do to lessen the damage it can cause. Unfortunately, a felony can potentially stay forever on your record.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will a 20 Year Old Felony Show Up on a Background Check?
It depends. Some states have a 7-10 year lookback period which means a 20 years felony will not show up. Other states have no set limits on how long a felony stays on a background check. Some states also allow felony convictions to show up indefinitely, but felony non-convictions will not be visible to the public.
Will a Felony Show Up on a Background Check After 10 Years?
In states with a seven year lookback period, a felony will not show up on a background check. Currently Arizona, California, Colorado, Hawaii, Kansas, Maryland, Massachusetts, Montana, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Mexico, New York, Texas and Washington limit background checks regarding criminal history to 7 years.
How Long Does a Class C Felony Stay on Your Record?
Laws from state to state vary on how long a felony stays on record. Some states have 7-10 year lookback periods. Others have no limitations. For felony non-convictions, the FCRA places a seven year limit on how far felony records can be considered.
1 America’s Invisible Felon Population. (2019, May 22). Joint Economic Committee. Retrieved August 15, 2022, from <https://www.jec.senate.gov/public/_cache/files/b23fea23-8e98-4bcd-aeed-edcc061a4bc0/testimony-eberstadt-final.pdf>
2 Using Consumer Reports for Credit Decisions: What to Know About Adverse Action and Risk-Based Pricing Notices. (n.d.). Federal Trade Commission. Retrieved August 15, 2022, from <https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/using-consumer-reports-credit-decisions-what-know-about-adverse-action-risk-based-pricing-notices>
3 Enforcement Guidance on the Consideration of Arrest and Conviction Records in Employment Decisions under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act. (2012, April 25). Equal Employment Opportunity Commission. Retrieved August 15, 2022, from <https://www.eeoc.gov/laws/guidance/enforcement-guidance-consideration-arrest-and-conviction-records-employment-decisions>
4 Criminal Offense Levels – MN House Research. (n.d.). Minnesota House of Representatives. Retrieved August 15, 2022, from <https://www.house.leg.state.mn.us/hrd/issinfo/cr-offn.aspx>
5 Fair Credit Reporting Act. (n.d.). Federal Trade Commission. Retrieved August 15, 2022, from <https://www.ftc.gov/system/files/documents/statutes/fair-credit-reporting-act/545a_fair-credit-reporting-act-0918.pdf>
6 guide, s. (n.d.). eCourts Expungement System. NJ Courts. Retrieved August 15, 2022, from <https://www.njcourts.gov/selfhelp/expungement.html>
7 Criminal Record Expungements. (n.d.). Oklahoma State Bureau of Investigation |. Retrieved August 15, 2022, from <https://osbi.ok.gov/sites/g/files/gmc476/f/documents/Criminal_Record_Expungement_TRIFOLD_11-2019_0.pdf>
8 Clean Your Record – criminal_selfhelp. (n.d.). California Courts. Retrieved August 15, 2022, from <https://www.courts.ca.gov/1070.htm?rdeLocaleAttr=en>











